Photonic Transport Network Systems Project
We are engaged in research, development, and maintenance of link systems, service systems, and control systems to advance APN transport and existing transport systems.
Technology related to optical transmission networks
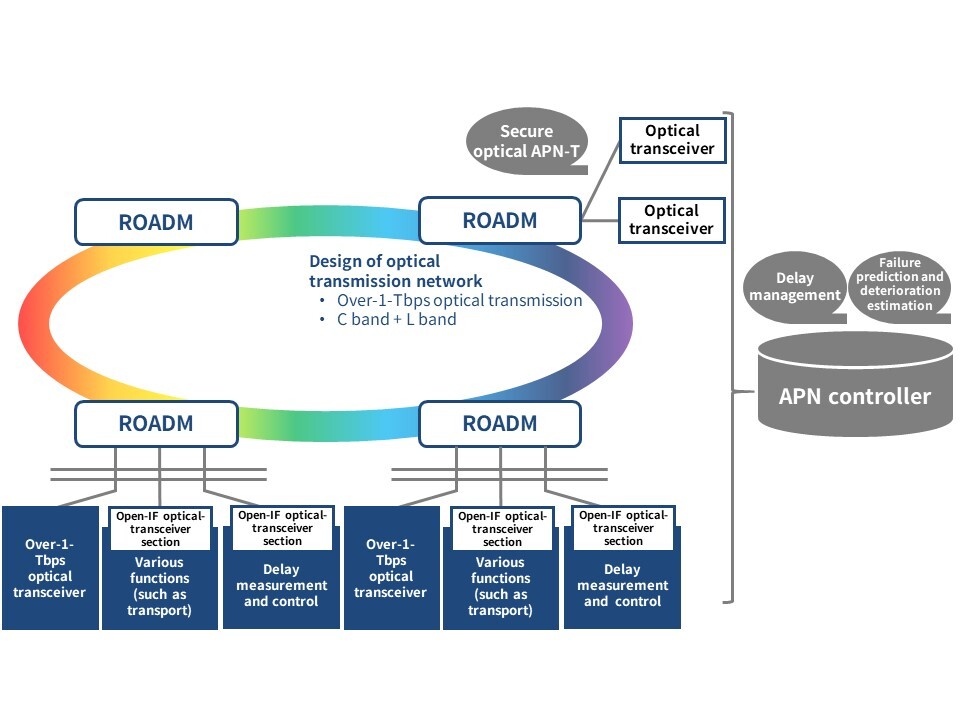
To advance and expand the use of the APN*1, which is the foundation of the IOWN, we are striving to increase the speed and capacity of optical transmission networks, make optical interfaces “open,” and add value to APN networks by making them low latency and highly secure. As for the advancement of optical transmission networks, multiplexing optical signals across multiple wavelength bands—by utilizing high-density wavelength-multiplexing technology and digital-coherent technology—makes it possible to increase transmission capacity. Moreover, separating the ROADM*2 function and the optical transmission/reception function and creating an open optical interface between them makes it possible to connect to remote locations using optical signals.
*1 APN: All-Photonics Networ
*2 ROADM: Re-configurable Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer
Related information
White-box NOS technology
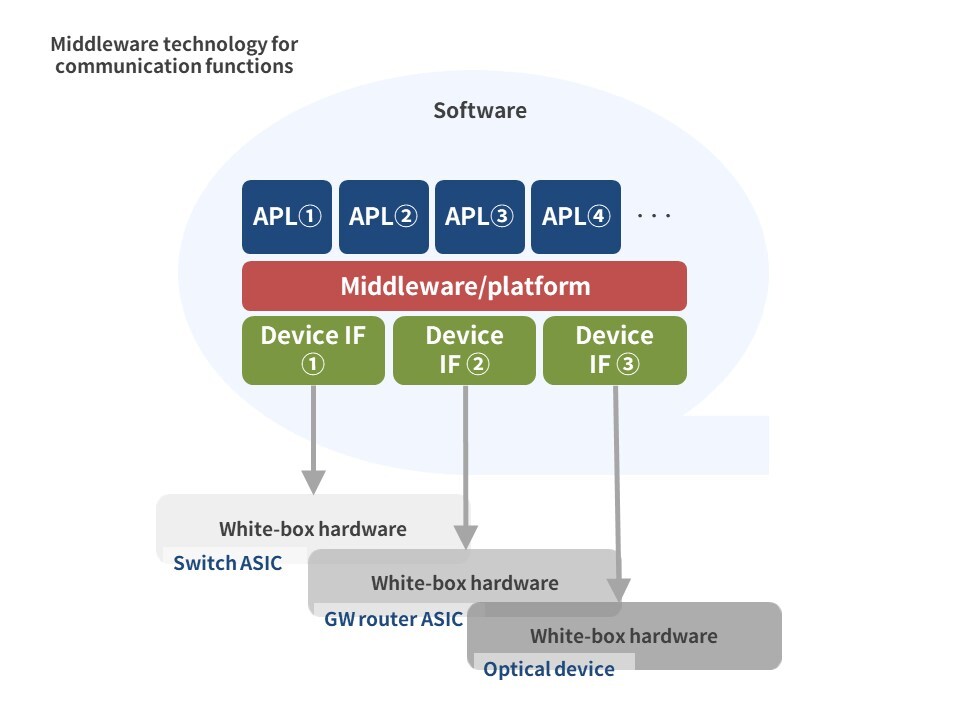
Beluganos, namely, a white-box-control NOS*1, is equipped with an optical coherent module and enables wavelength connection to the APN. By making Beluganos NTT’s in-house NOS for carriers, we will be able to achieve cost-effectiveness by utilizing white-box switches and will be able to adapt Beluganos to service requirements by adding unique functions to it. Moreover, focusing on a technology for the future, we are working on “Open Middleware,” namely, a middleware technology for communication functions that uses highly modular software technology to more easily respond to requirements for diverse communication services. *1 NOS: NetworkOS
Related information
- Research & Activity: “Network OS for NTT In-house White-box Switch: Beluganos”
Technology related to APN controller
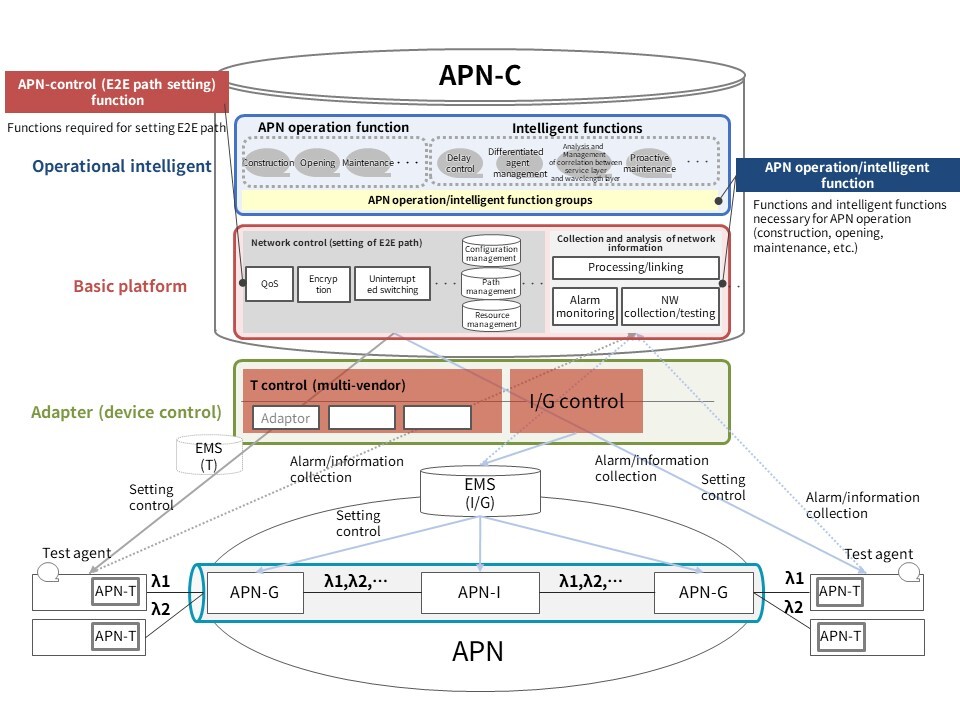
The APN controller (APN-C), which handles network operation and quality control, is one of the key elements in implementing the APN*1, which is the foundation of the IOWN. The APN-C consists of three layers: (i) “basic platform,” which has network-control and information-collection-and-analysis functions and serves as the foundation for E2E path setting and monitoring; (ii) “operational intelligence,” which provides quick and stable functions required for APN operation; and (iii) “adapter (device control),” which coordinates settings of the APN-C, devices, and NE-OpS*2 to seamlessly connect optical transmission networks and the APN-T.
*1 APN: All-Photonics Network
*2 NE-OpS: Network Element-Operations System
Related information
- Research & Activity: “APN Controller Technology for Providing and Expanding IOWN Services”
- NTT Technical Review: “APN-controller Technology for IOWN Service Provision and Expansion”
- APN: All-Photonics Network