Network Control Software Project
We are engaged in research and development of software technologies that support server systems as infrastructure.
Automated control of virtualization infrastructure: ORCHESTRA
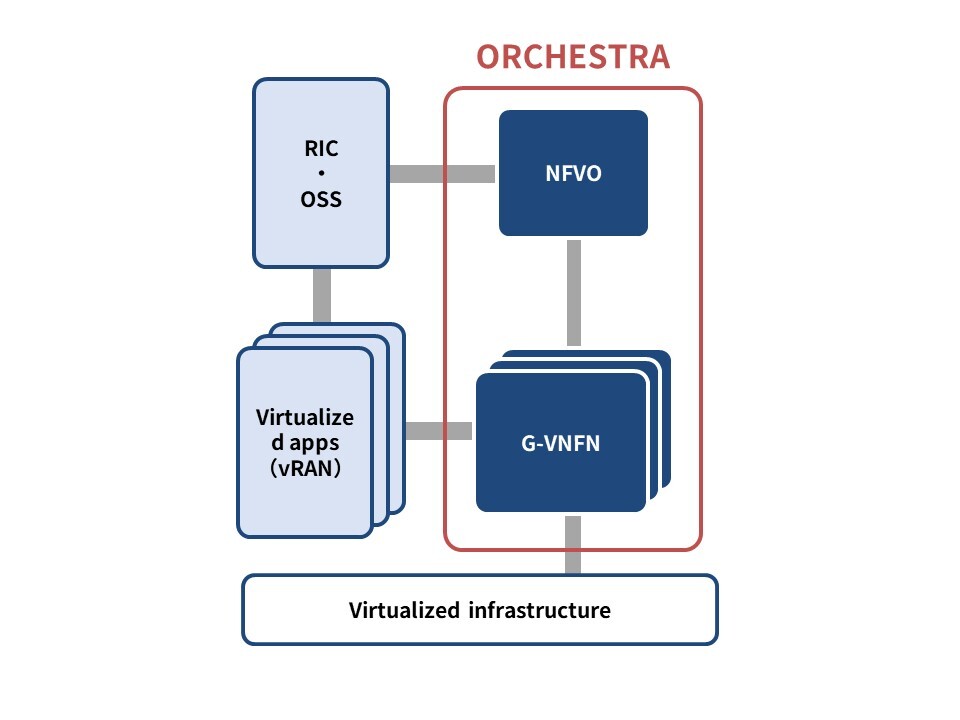
ORCHESTRA is a virtualization control function unit (MANO*1 function) specified by ETSI NFV, and we are currently developing it for application to vRAN*3 systems based on O-RAN*2 specifications. In cooperation with OSS/BSS*4, it provides LCM*5 functions that automatically control dynamic construction, deployment, operation, and termination of applications on virtualization platforms. In conjunction with this development, we are also promoting OSS activities concerning OpenStack Tacker and CNCF*6, popularizing the use of ORCHESTRA, and ensuring its interoperability at the implementation level with various applications.
*1 MANO: Management and Orchestration
*2 O-RAN: Open Radio Access Network
*3 vRAN: virtual RAN
*4 OSS/BSS: Operation Support System / Business Support System
*5 LCM: Life-Cycle Management
*6 CNCF: Cloud Native Computing Foundation
Related information
- O-RAN Alliance
- ETSI NFV
- Openstack Tacker
- CNCF
- NTT Technical Review: “Initiatives toward Open RAN”
- NTT Technical Review: “Initiatives toward Virtualized RAN”
- NTT Technical Review: “Initiatives toward Intelligent RAN”
Power-aware dynamic-allocation control (PADAC) technology
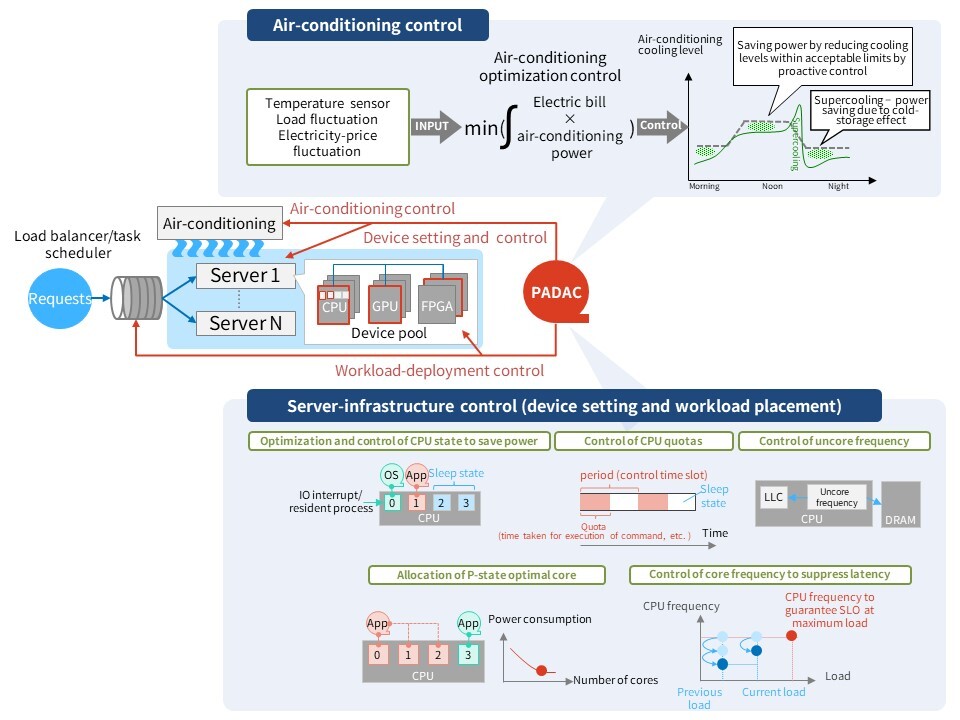
Power-aware dynamic-allocation control (PADAC*1) is a technology that can maximize power efficiency by software control of server infrastructure in a way that reduces power consumption. The key feature of PADAC is that it can be applied without modifying the software of existing systems. By allocating and setting loads according to the power characteristics of computing devices such as CPUs and optimizing the cooling efficiency of air conditioning and servers in data centers, it is possible to control power savings in the entire data center. *1 PADAC: Power-Aware Dynamic Allocation Control
Related information
Embedded power-saving enabler (POSENA)
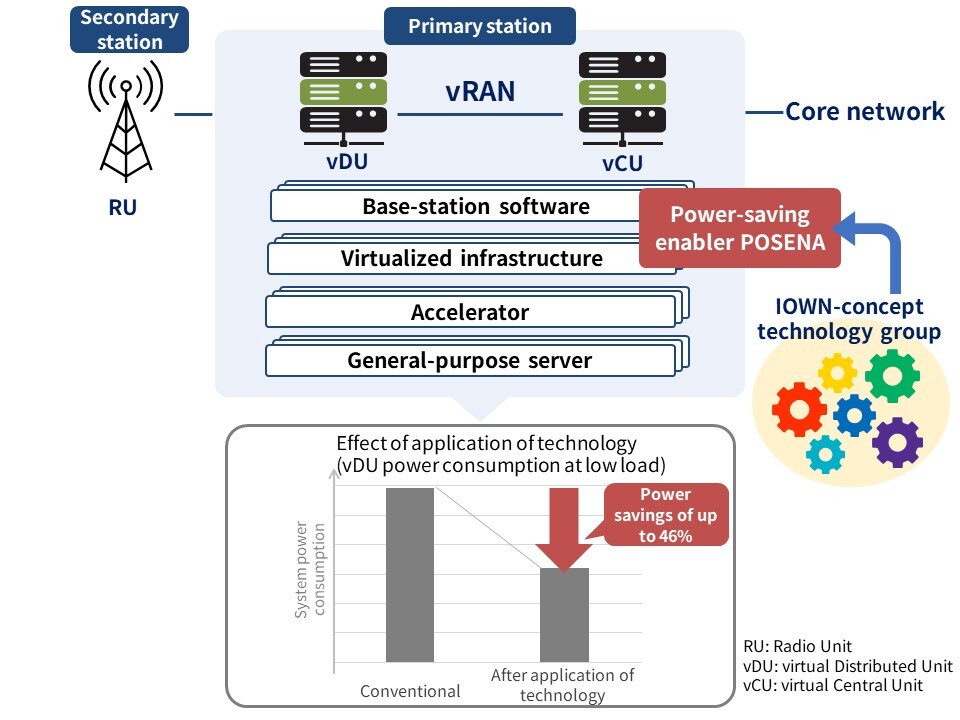
POSENA*1 is a software power-saving implementation technology that allows developers to save power while meeting high-performance requirements with general-purpose servers. Software that requires high performance tends to consume more computing resources than necessary; however, POSENA enables processing with the minimum computing resources required for the load, and it has a particularly large power-saving effect at low loads. Currently, we are analyzing each software process of vRAN*2, devising, implementing, and evaluating techniques to improve power-inefficient processing, and demonstrating that it is possible to save power without degrading performance.
*1 POSENA: POwer Saving ENAbler
*2 vRAN: virtual RAN
Related information
Security Handler for Efficient Protection and HARDening (SHEPHARD)
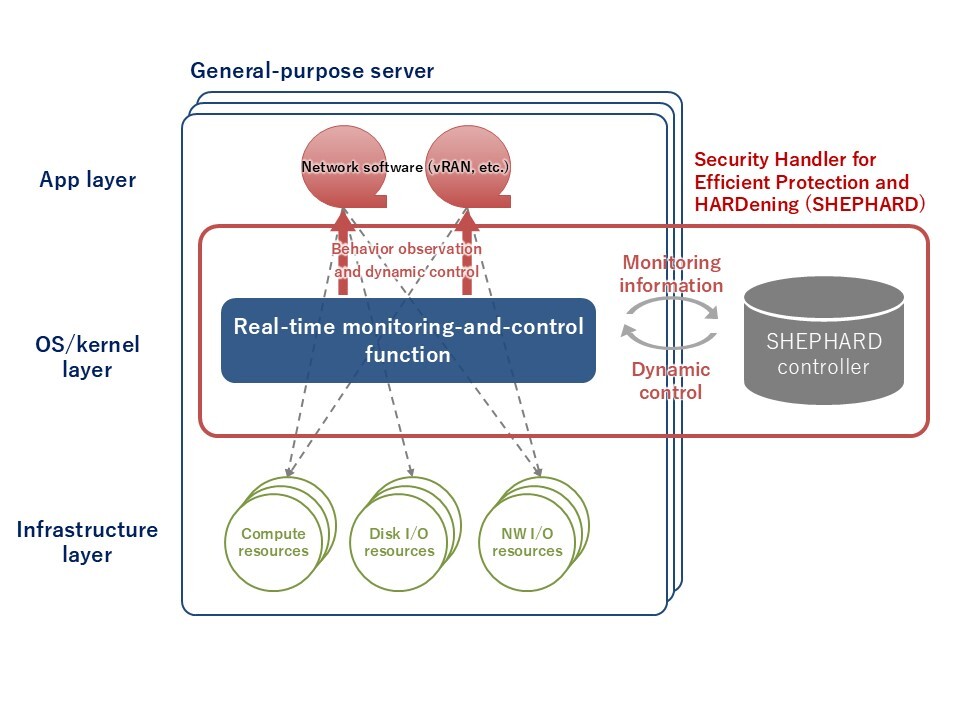
SHEPHARD*1 is a technology that implements security measures according to operational conditions by monitoring, analyzing, and controlling the OS level. It consists of a “real-time monitoring and control function”—which monitors and controls software on the host OS—and a “controller”—which analyzes effects of that software control and makes control decisions on the basis of collected information and the overall status of the network. Real-time monitoring of security risks is a challenge owing to the processing load of the monitored objects; however, SHEPHARD adjusts the monitoring level according to the load in a manner that makes it possible to provide advanced security added value even under high-performance requirements.
*1 SHEPHARD: Security Handler for Efficient Protection and HARDening
Communication platform that supports metacommunication (immersive RTC platform)
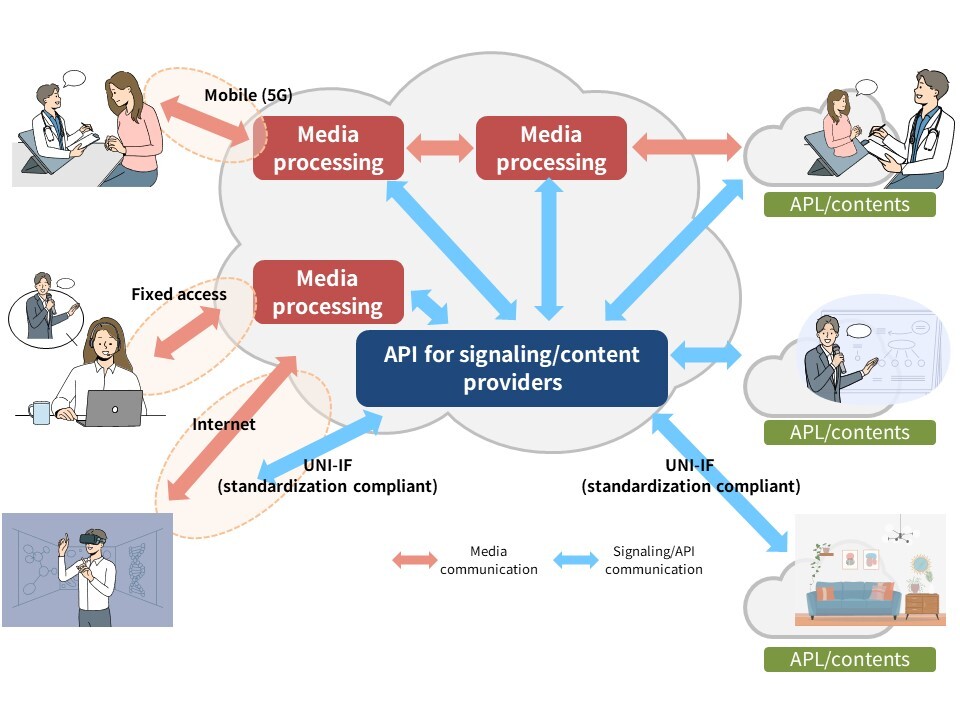
As a communication platform, the immersive RTC platform supports metacommunication services for both mobile and fixed networks, and it is compliant with 3GPP standardization to achieve high interoperability. It uses a cloud-native distributed architecture, which provides scalability and flexibility for adding functions , and enables signaling control and media-processing allocation control that can be adapted to various service patterns. Allowing content providers to focus on developing content, this platform is expected to revitalize the metacommunication-service market.
*1 RTC: Real-Time Communication
Related information
- NTT Technical Review: “Standardization Trends in Real-time Communications at 3GPP”